Drone Delivery Path Optimization
Optimize delivery of packages using algorithms like A*, MDP, etc.
The growing demand for fast, reliable, and cost-effective package delivery services has created significant challenges for logistics and transportation networks. Companies must navigate complex systems involving large fleets, dynamic traffic conditions, and diverse customer demands. Traditional manual planning methods often fall short in addressing these complexities, leading to inefficiencies, increased costs, and delays. Optimizing delivery routes and schedules using advanced algorithms offers a promising solution, enabling smarter decision-making and improved operational efficiency. With the rise of e-commerce and urban congestion, the need for innovative, algorithm-driven approaches has never been more critical.
Algorithms such as A* and Markov Decision Processes (MDPs) are well-suited to tackle these challenges. A*, a heuristic-based search algorithm, efficiently finds the shortest paths in static or semi-static environments, making it ideal for real-time route optimization. Meanwhile, MDPs provide a framework for making sequential decisions under uncertainty, allowing systems to adapt dynamically to changing traffic patterns or delivery constraints. By leveraging these advanced methods, this project aims to simulate and attempts to enhance package delivery systems, reducing operational costs and delivery times while improving customer satisfaction.
The project environment was set up as the following:
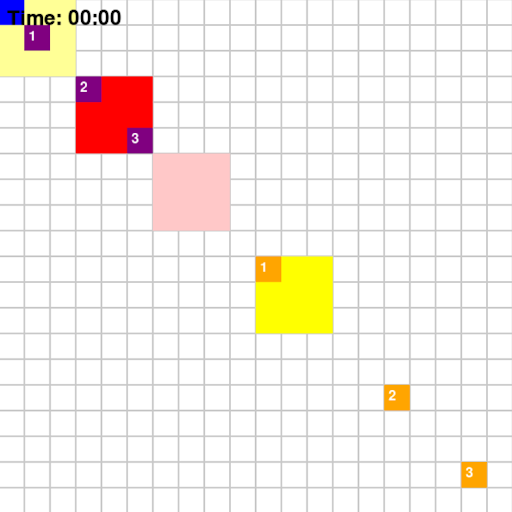
Each agent will traverse a grid map with deliverables marked in dark blue and drop-off marked in orange. To increase the complexity of the problem, the environmnet will be dynamic which means that every few steps, the positions of obstacles and restrictions will change. The map for the game looks like the following:
Taking the above map as an example, the path that agents implemented using different algorithms took are shown below
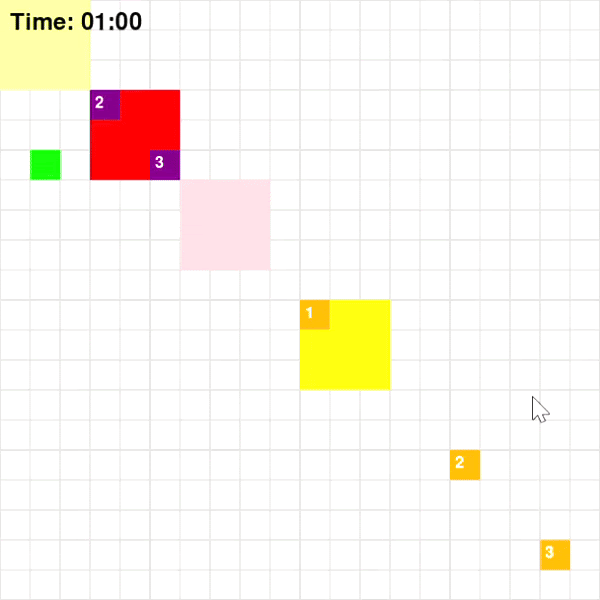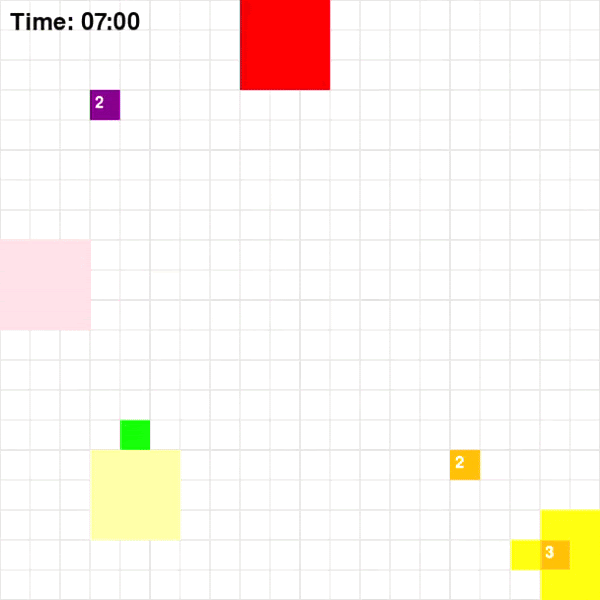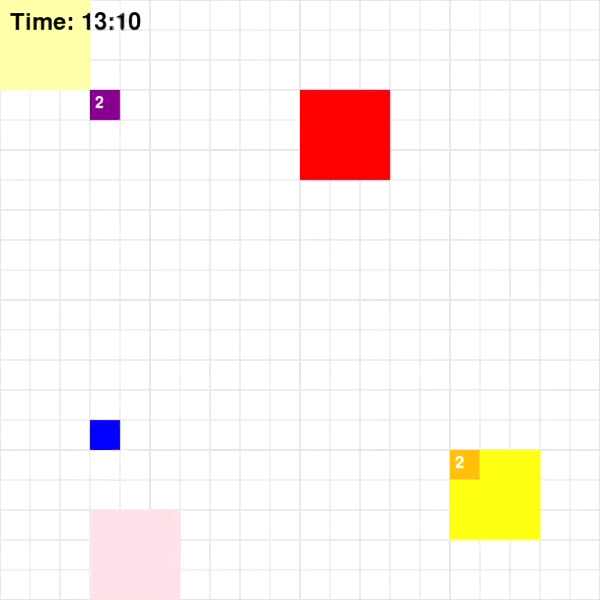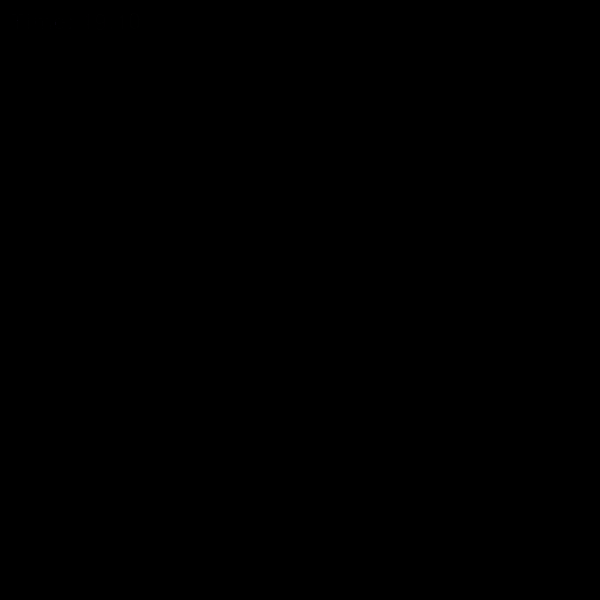
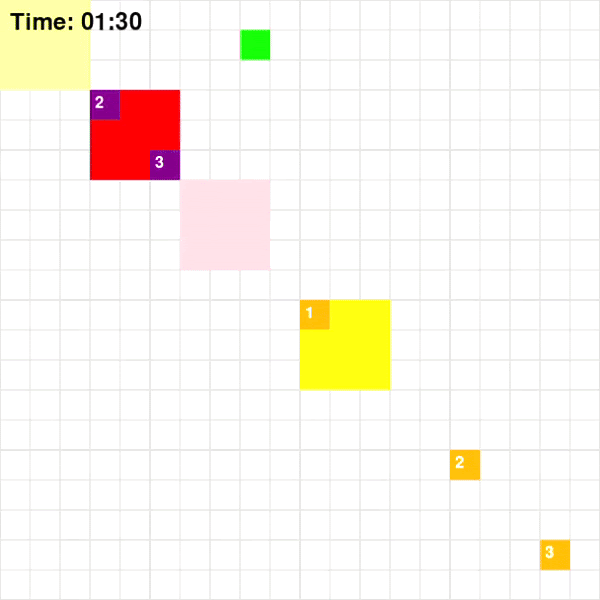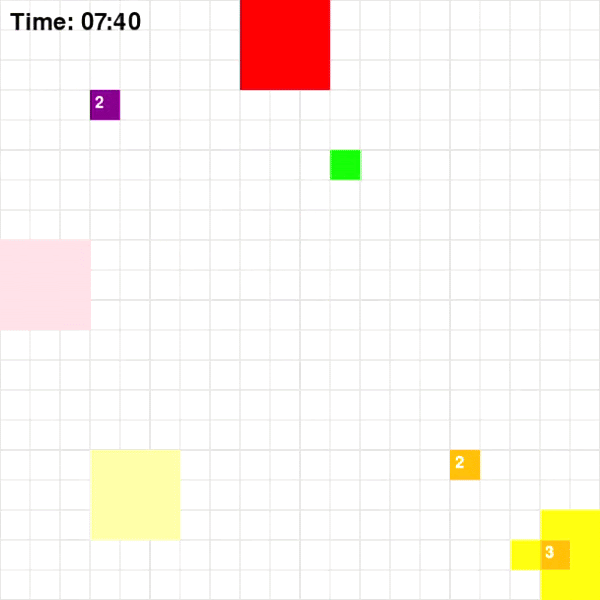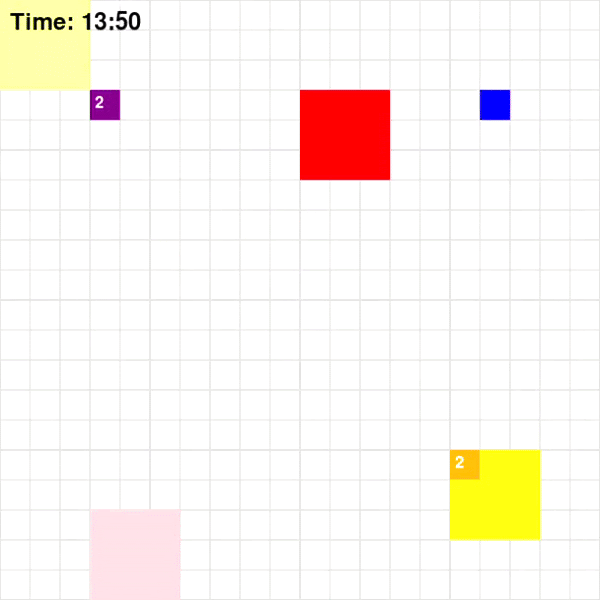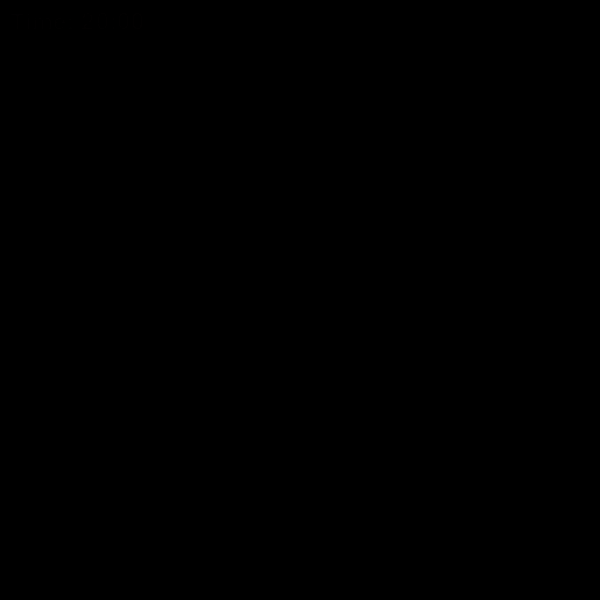
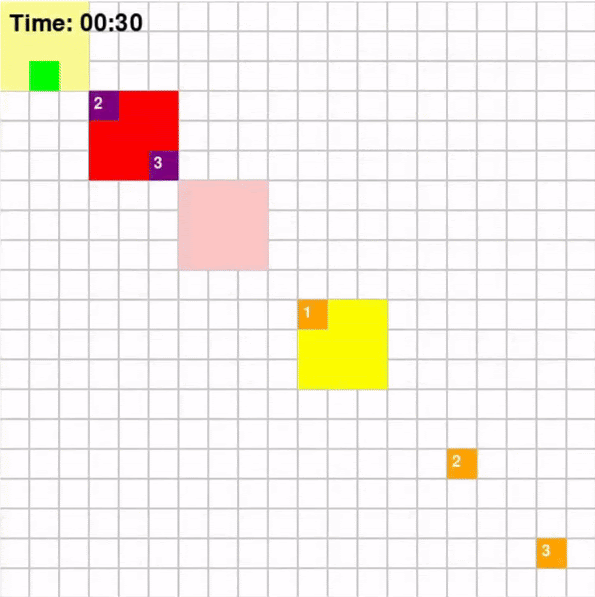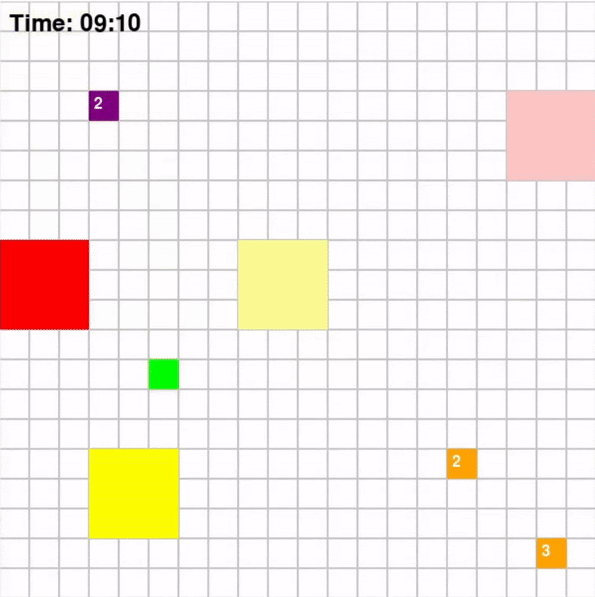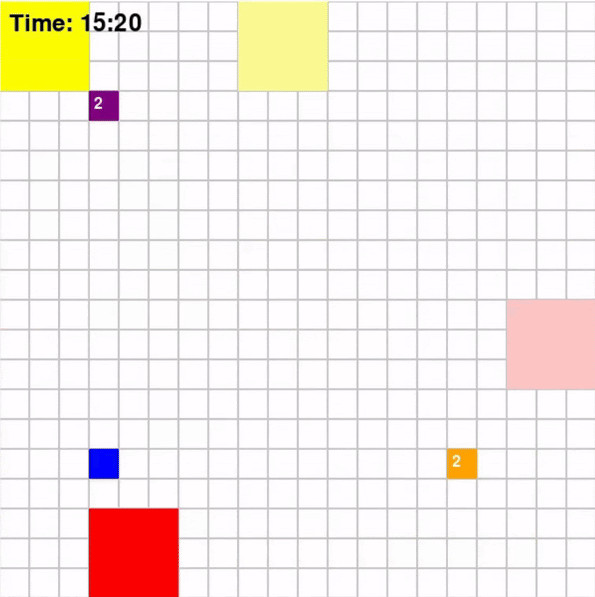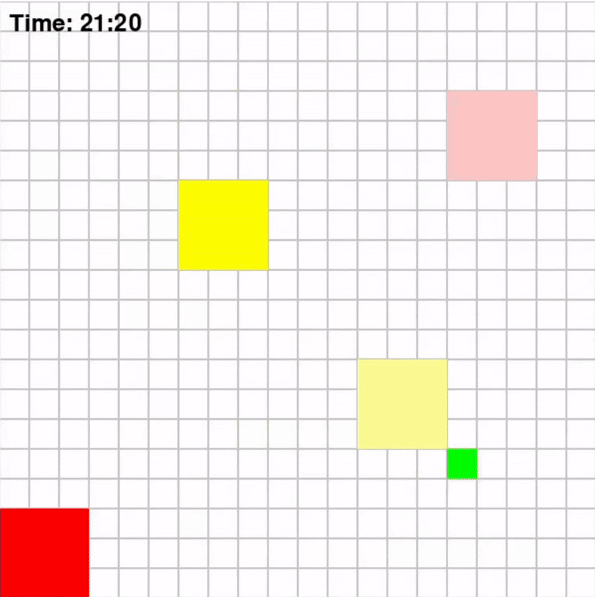
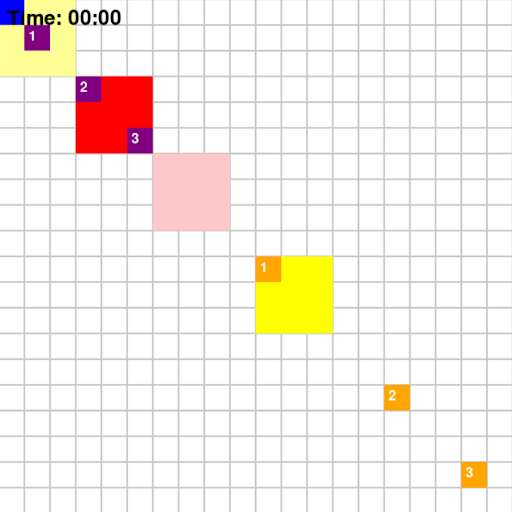
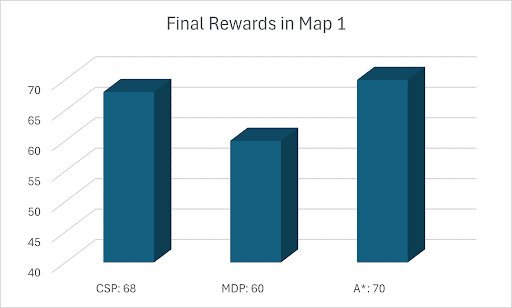
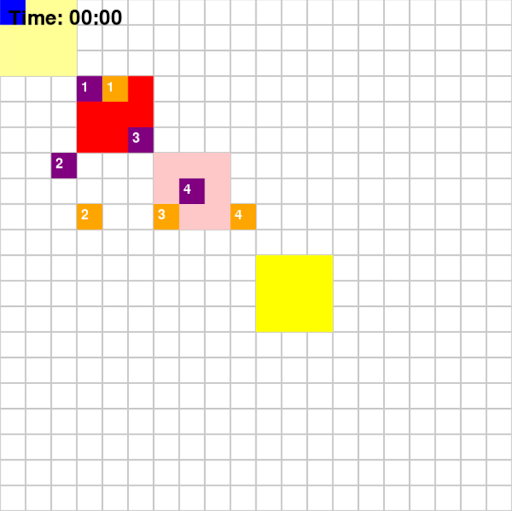

Base on Figure 3 and 4, for Map 1, A* algorithm achieved the best score of 70 while MDP achieved the lowest score of 60. Given that Map 1 is a simplistic map with very few optimal paths from each pick-up point to drop-off points, A* should intuitively be more optimal since A* is a shortest path algorithm. For Map 2, CSP achieved the highest rewards of 205 while MDP and A* achieved rewards of 193. This could be the result of the fact that these two algorithms are superior at adapting to a dynamic environment.
For more information about the project, the project page can be accessed at:
---
https://github.com/chengq220/CS4260_FinalProject
---